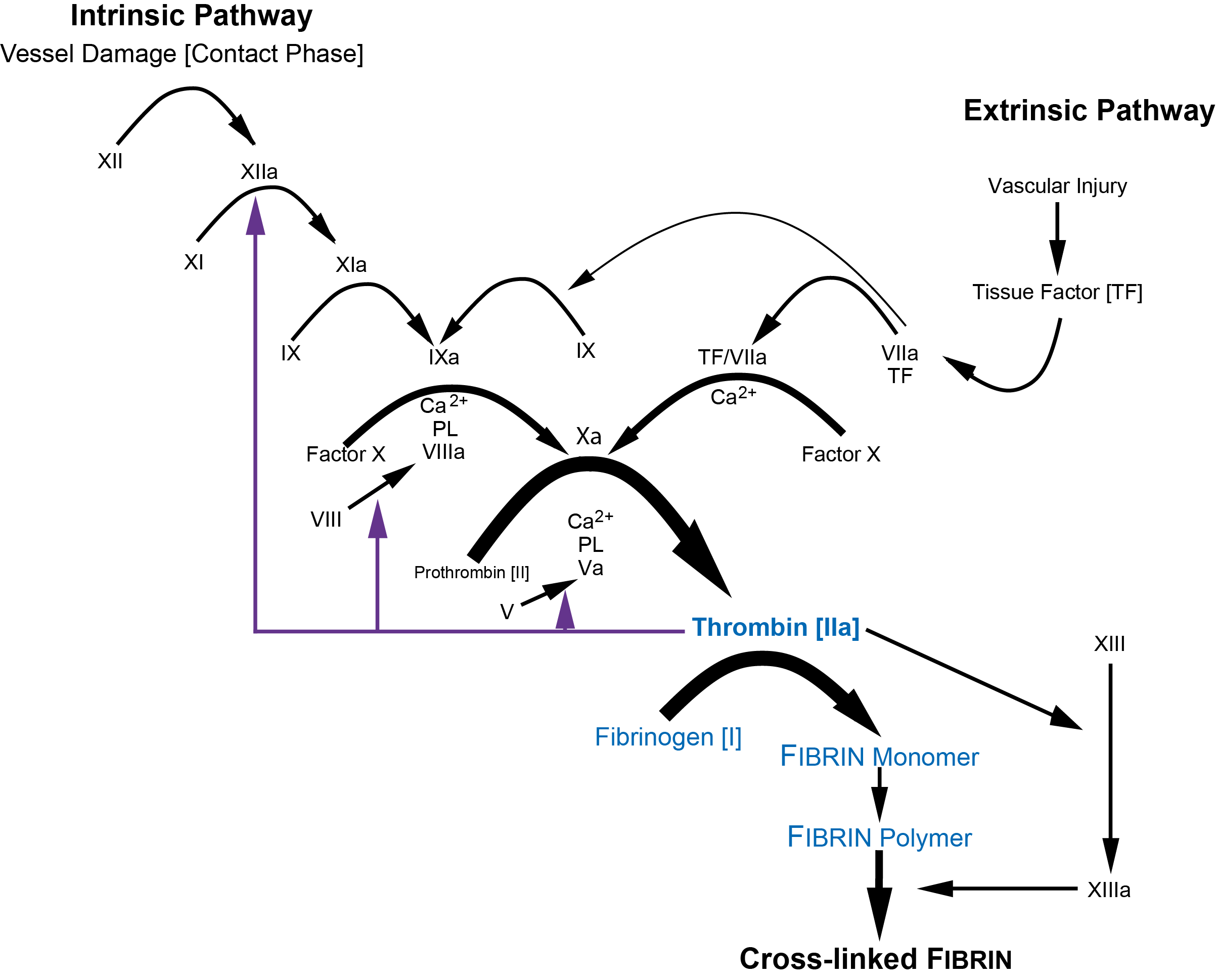
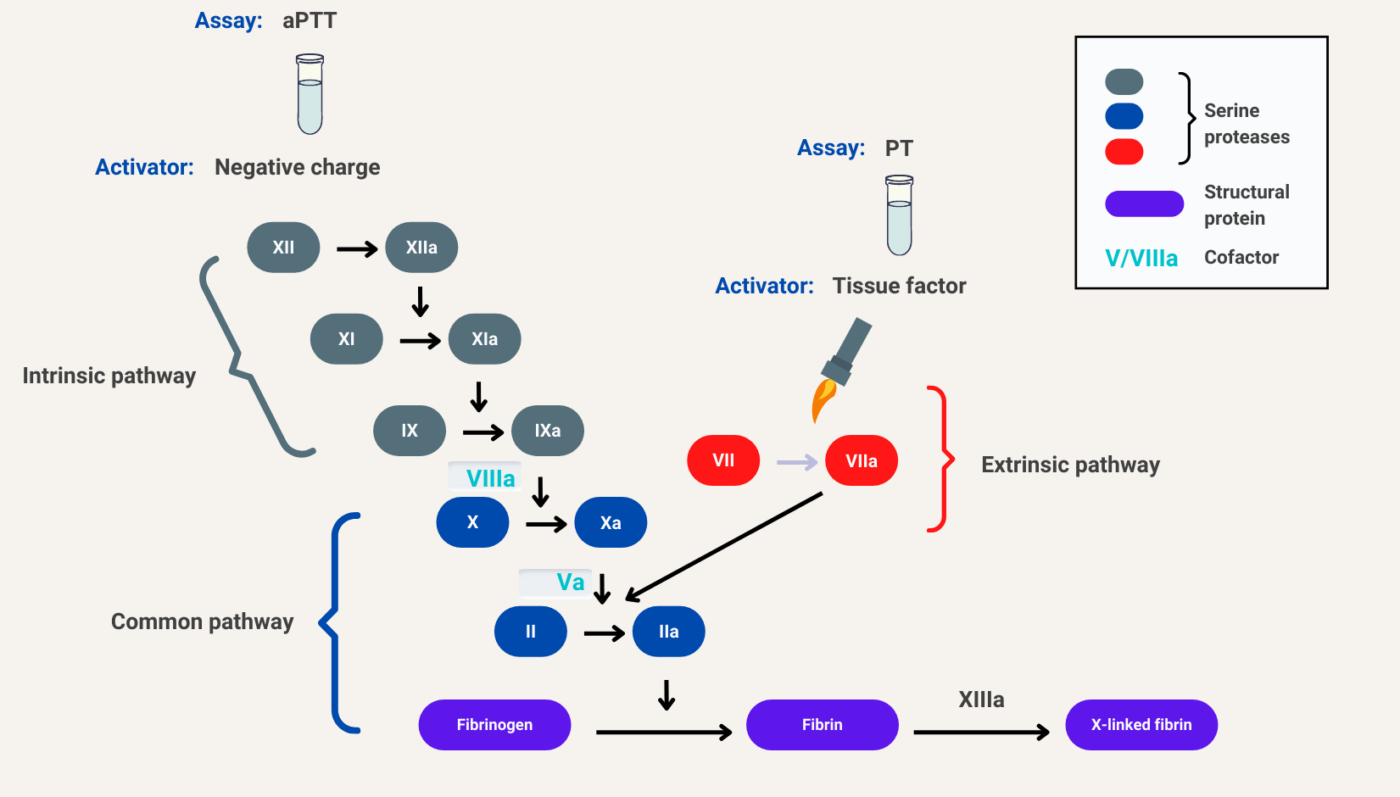
What Role Does The Enzyme Thrombin Play In Blood Clotting
What Role Does The Enzyme Thrombin Play In Blood Clotting - The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c. The last enzyme in the coagulation. Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation.
Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c. The last enzyme in the coagulation. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation.
Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. The last enzyme in the coagulation. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c.
Difference Between Intrinsic and Extrinsic Pathway in Blood Clotting
Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c. The last enzyme in the coagulation. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. Thrombin is a.
Screening Tests in Haemostasis The Thrombin Time
Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. The last enzyme in the.
Blood Clotting Biology AS Level HubPages
The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. The last enzyme in the coagulation. Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin.
What is the clotting cascade? • The Blood Project
Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c. The last enzyme in the coagulation. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and.
Question Video Explaining the Role of Thrombin in Blood Clotting Nagwa
Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. The last enzyme in the coagulation. Thrombin is a.
Thrombin enzyme molecule, illustration Stock Image F019/2415
The last enzyme in the coagulation. Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and.
Question Video Explaining the Role of Thromboplastin in Blood Clotting
Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c. Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in.
Clotting BioNinja
Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. The last enzyme in the coagulation. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the.
Ficha coagulation cascade ENALLTerm
The last enzyme in the coagulation. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin.
Pin on Igcse biology
The last enzyme in the coagulation. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating. Thrombin also plays a role in plasmin’s inactivation, stimulating activity of thrombin activatable fibrinolysis inhibitor. Thrombin is a.
The Last Enzyme In The Coagulation.
Thrombin is a key intermediate in the coagulation cascade, because it activates upstream procoagulant factors to amplify the coagulation. The generation of thrombin in coagulation plays a central role in the functioning of haemostasis. Upon interacting with thrombin, thrombomodulin converts it into an anticoagulant enzyme by activating protein c. The serine protease thrombin, a naturally derived enzyme, plays a key role in hemostasis by converting fibrinogen to fibrin and activating.