Sandwich Theorem Khan Academy
Sandwich Theorem Khan Academy - When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization.
Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard. Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now:
Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be.
Sandwich Theorem or Squeeze Theorem Statement with Proof
When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; Practice this lesson yourself on.
Sandwich Theorem or Squeeze Play Theorem for Evaluating Limits
Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. Practice this lesson yourself on.
Sec. 1.3 Evaluating Limits Analytically ppt download
Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard. When a sequence lies between two.
Sandwich Theorem Scrolller
When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers,.
Proof of the Sandwich Theorem and Visualization YouTube
When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem.
Sandwich Theorem in Mathematics. HubPages
Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard. Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. When a sequence.
Properties of Limits. ppt download
When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard. Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x).
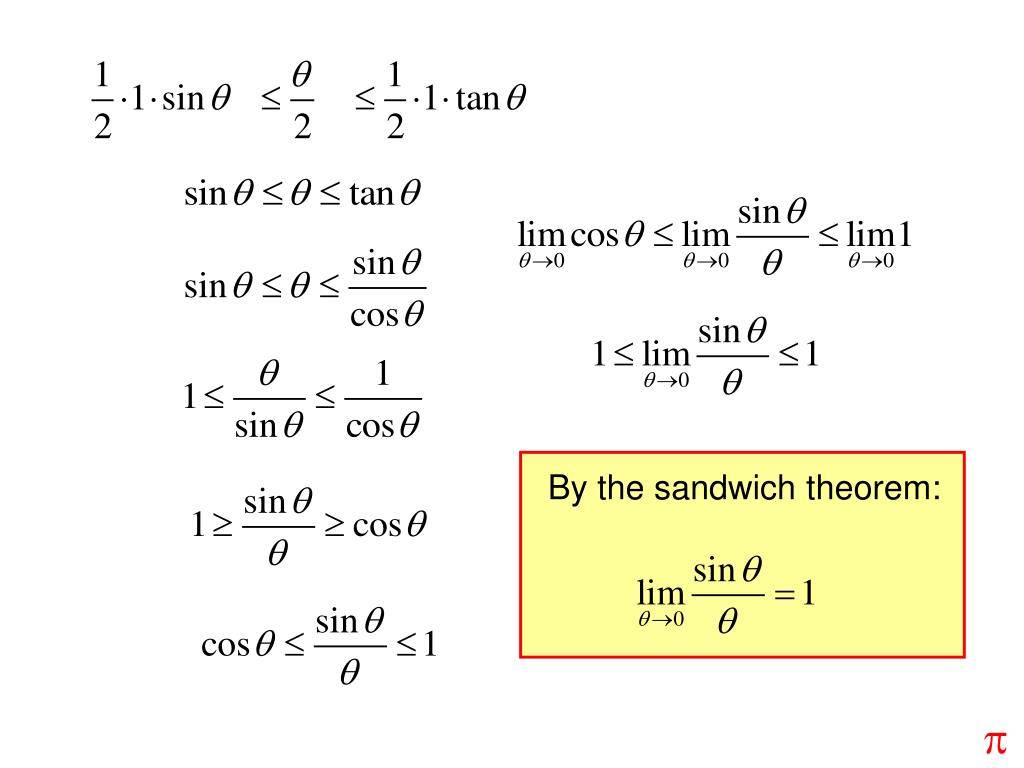
Squeeze theorem or sandwich theorem Limits Differential Calculus
Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; When a sequence lies between two other.
Squeeze theorem or sandwich theorem Limits Differential Calculus
Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and.
PPT Using the Sandwich theorem to find PowerPoint Presentation, free
When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be. The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point.
Practice This Lesson Yourself On Khanacademy.org Right Now:
When a sequence lies between two other converging sequences with the same limit, it also converges to this limit. Khan academy is a 501 (c) (3) nonprofit organization. Certain limits which cannot be determined directly can be determined indirectly; Khan academy offers practice exercises, instructional videos, and a personalized learning dashboard.
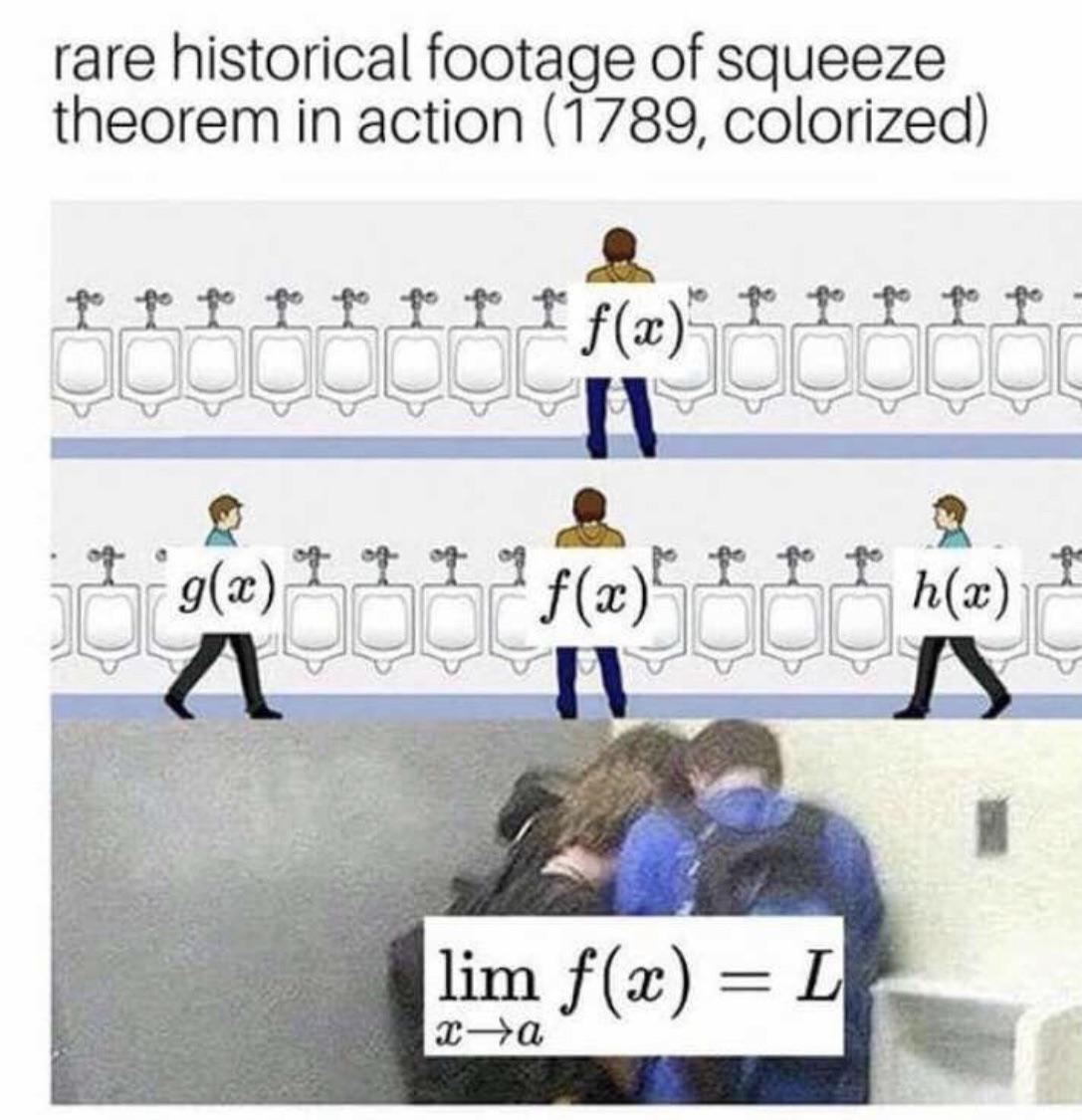
The Squeeze (Or Sandwich) Theorem States That If F(X)≤G(X)≤H(X) For All Numbers, And At Some Point X=K We Have F(K)=H(K), Then G(K) Must Also Be.
The squeeze (or sandwich) theorem states that if f(x)≤g(x)≤h(x) for all numbers, and at some point x=k we have f(k)=h(k), then g(k) must also be.