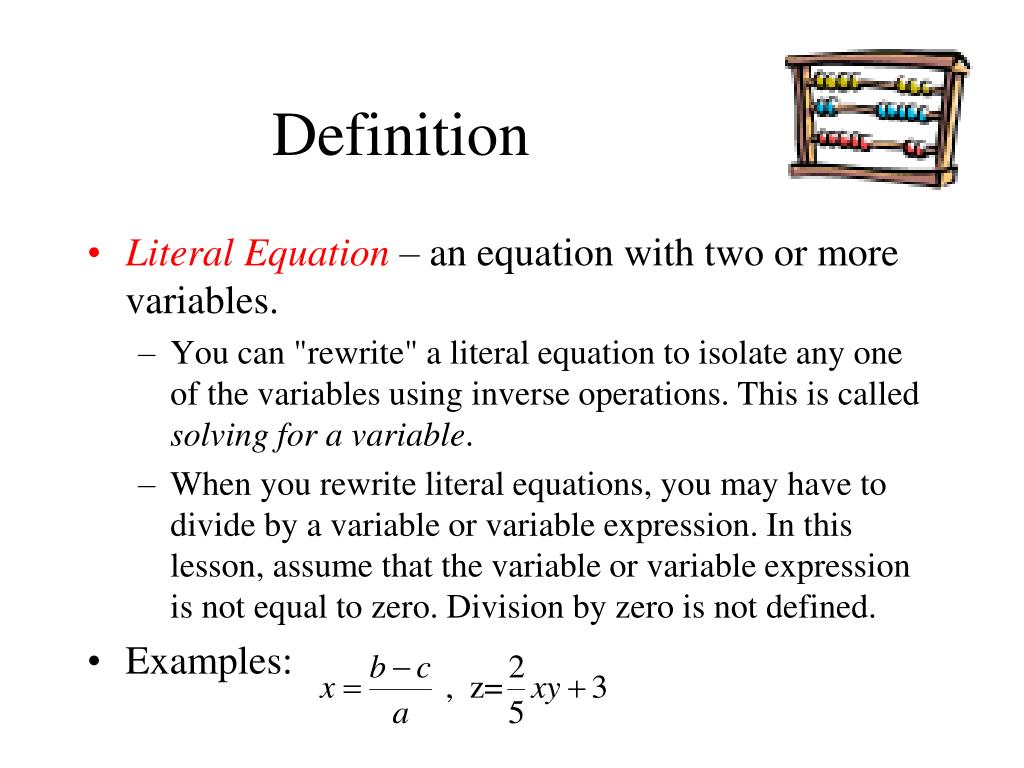
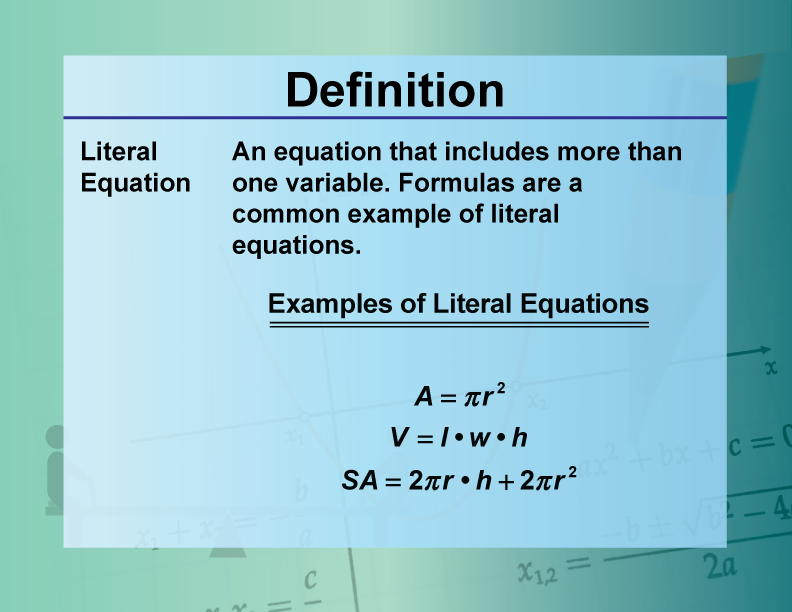
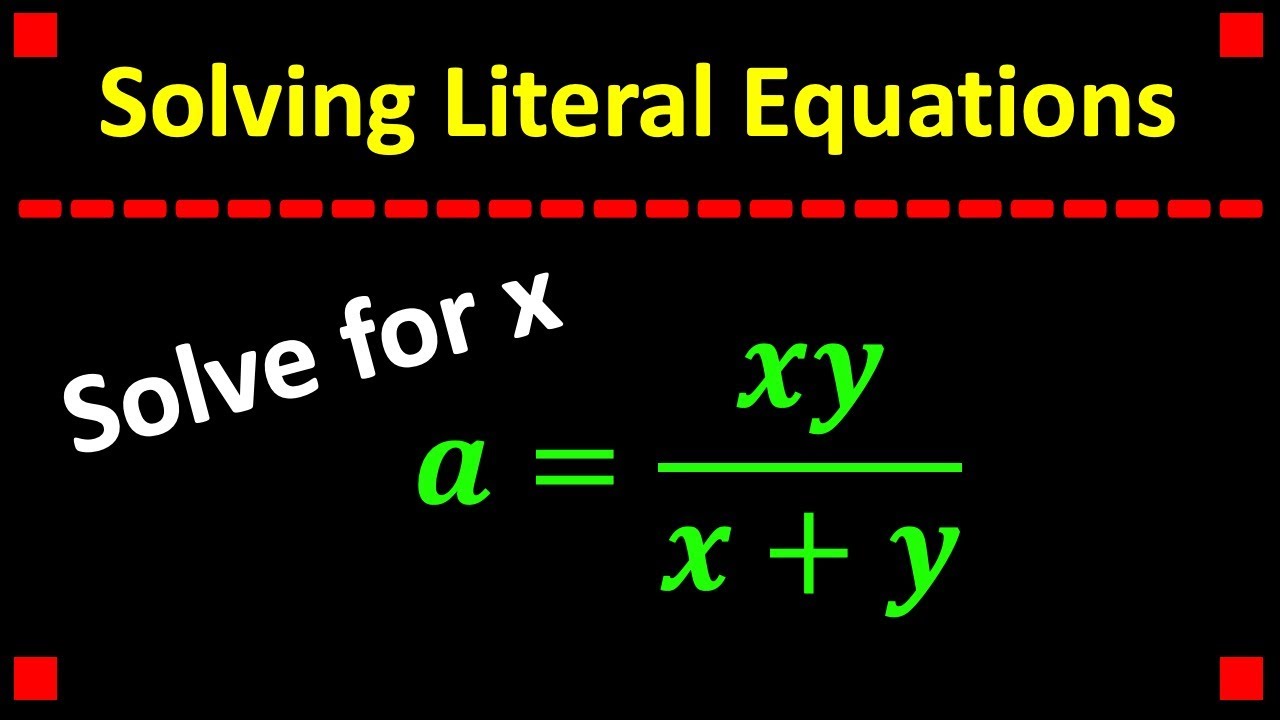Literal Equation Definition Math
Literal Equation Definition Math - A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a.
A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities.
A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities.
Solving Literal Equations & Absolute Value Equations Mathematics
A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a.
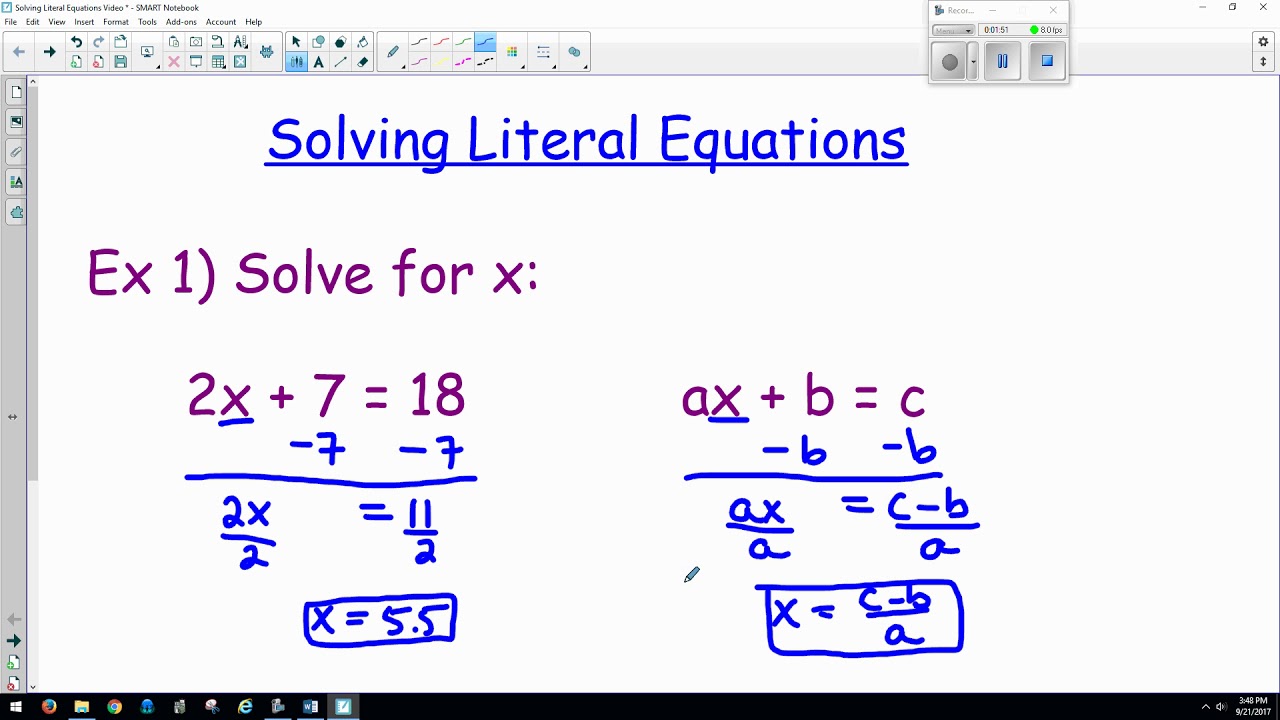
Solving Literal Equations YouTube
A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a.
ppt solving literal equations powerpoint presentation id422229
The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation.
Solving a Literal Equation YouTube
A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities.
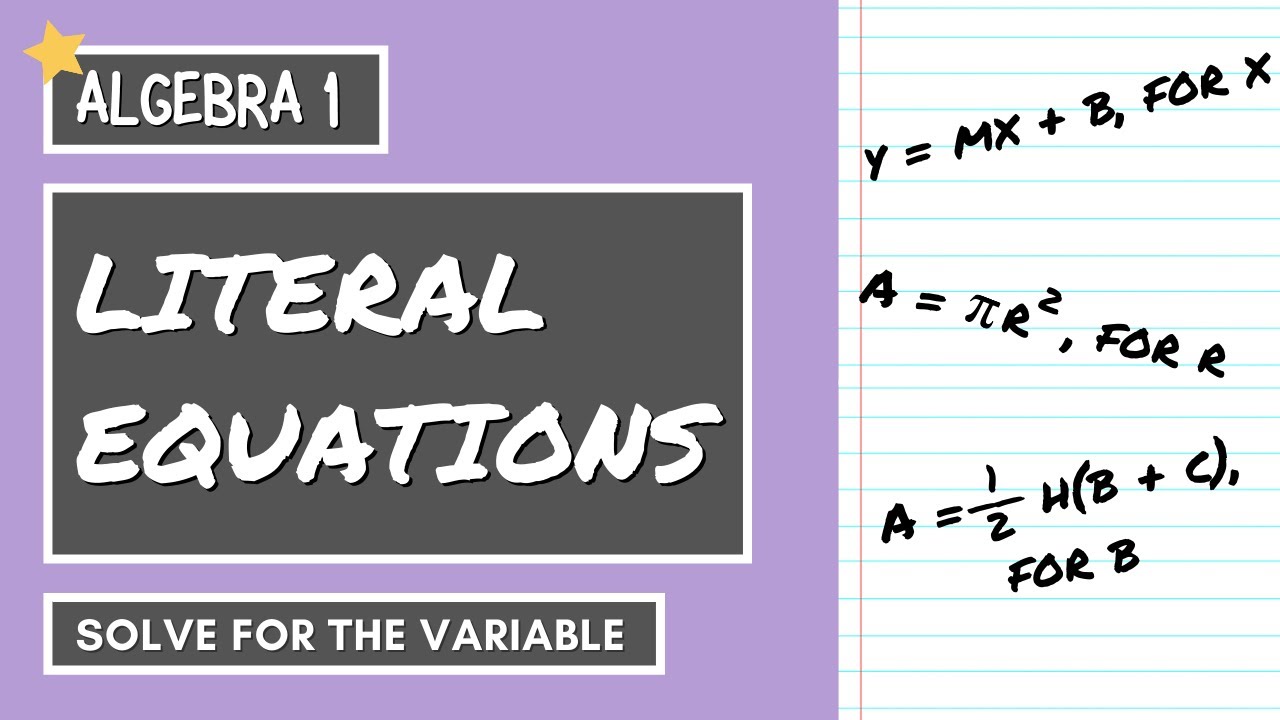
How to Solve LITERAL EQUATIONS ALGEBRA 1 YouTube
A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method.
Math Dyal Lovin' Literal Equations atelieryuwa.ciao.jp
A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a.
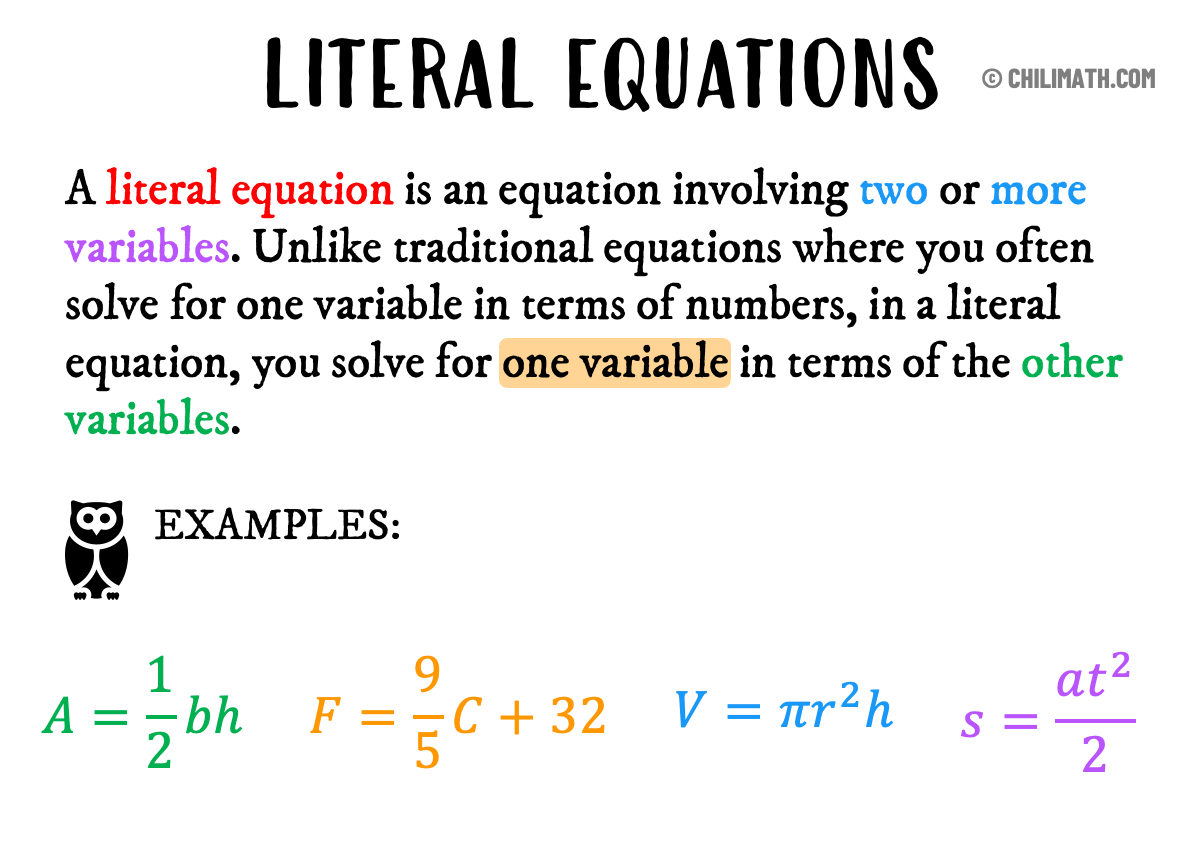
Literal Equations ChiliMath
A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities.
PPT Literal Equations and Formulas PowerPoint Presentation, free
The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation.
Literal Equations Literal equations, Maths solutions, Solving equations
A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method.
DefinitionEquation ConceptsLiteral Equation Media4Math
The purpose of a literal equation is to describe a. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities. A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation.
The Purpose Of A Literal Equation Is To Describe A.
A literal equation is synonymous with a formula and similar to solving general linear equations because we apply the same method. A literal equation is an equation that contains all letters (or variables) or an equation. A literal equation is an algebraic equation where the variables represent specific, measurable quantities.