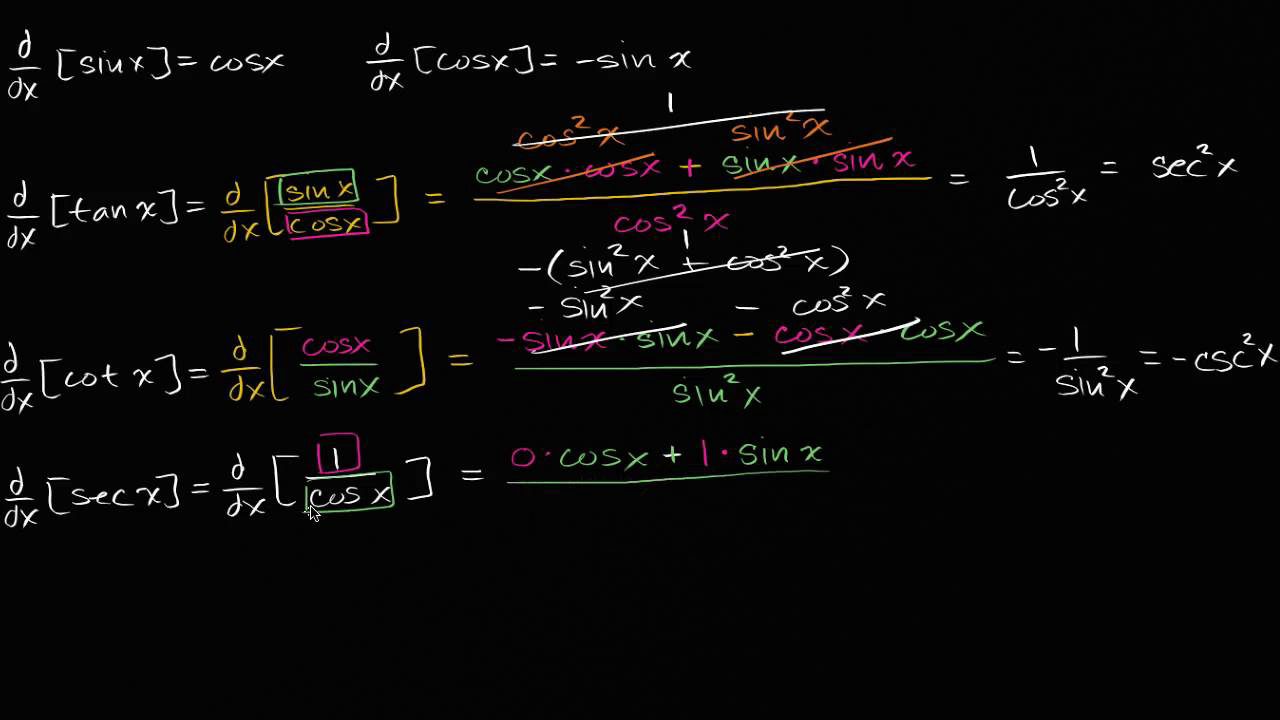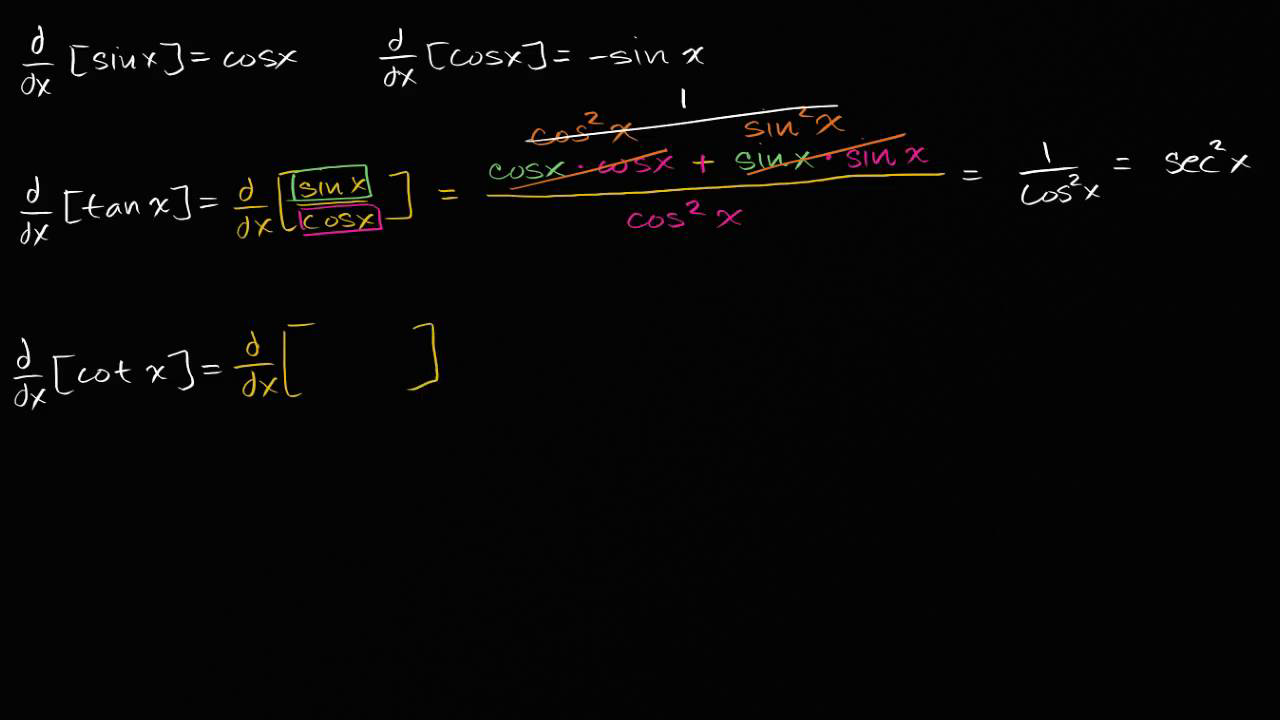Khan Academy Derivatives Practice
Khan Academy Derivatives Practice - If you're behind a web filter, please. Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. The big idea of differential calculus is the concept of the derivative, which essentially gives us the direction, or rate of change, of a function at any. Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. Consider the functions f and g with the graphs shown below. If f (x) = 3 f (x) − 2 g (x) , what is the value of f ′ (8) ? Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base a. Learn how to take derivatives in calculus with khan academy's comprehensive guide.
Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base a. If f (x) = 3 f (x) − 2 g (x) , what is the value of f ′ (8) ? The big idea of differential calculus is the concept of the derivative, which essentially gives us the direction, or rate of change, of a function at any. Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Consider the functions f and g with the graphs shown below. Learn how to take derivatives in calculus with khan academy's comprehensive guide. If you're behind a web filter, please.
Learn how to take derivatives in calculus with khan academy's comprehensive guide. The big idea of differential calculus is the concept of the derivative, which essentially gives us the direction, or rate of change, of a function at any. Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. If f (x) = 3 f (x) − 2 g (x) , what is the value of f ′ (8) ? Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base a. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Consider the functions f and g with the graphs shown below. If you're behind a web filter, please.
Derivative Practice 78 YouTube
Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. Consider the functions f and g with the graphs shown below. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please. Learn how to take derivatives.
Khan Academy
If you're behind a web filter, please. Consider the functions f and g with the graphs shown below. Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base.
Practice Sheet 11 Partial Derivatives PDF
The big idea of differential calculus is the concept of the derivative, which essentially gives us the direction, or rate of change, of a function at any. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base a. Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the.
Partial derivatives 2 Multivariable Calculus Khan Academy Partial
Learn how to take derivatives in calculus with khan academy's comprehensive guide. If f (x) = 3 f (x) − 2 g (x) , what is the value of f ′ (8) ? Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. Analyze derivatives of functions at.
Buy Essay UK Khan academy derivatives
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Learn how to take derivatives in calculus with khan academy's comprehensive guide. If you're behind a web filter, please. Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. Let's dive deeper.
Calculus Derivatives 2 Taking derivatives Differential Calculus
Consider the functions f and g with the graphs shown below. The big idea of differential calculus is the concept of the derivative, which essentially gives us the direction, or rate of change, of a function at any. Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. Here.
Derivative Rules
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base a. Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. The.
️Application Of Derivatives Practice Worksheet Free Download Goodimg.co
Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Learn.
Khan Academy Derivatives of Inverse Functions Instructional Video for
Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base a. If f (x) = 3 f (x) − 2 g (x) , what is the value of f.
Khan Academy
Learn how to take derivatives in calculus with khan academy's comprehensive guide. If f (x) = 3 f (x) − 2 g (x) , what is the value of f ′ (8) ? Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. If you're seeing this message, it.
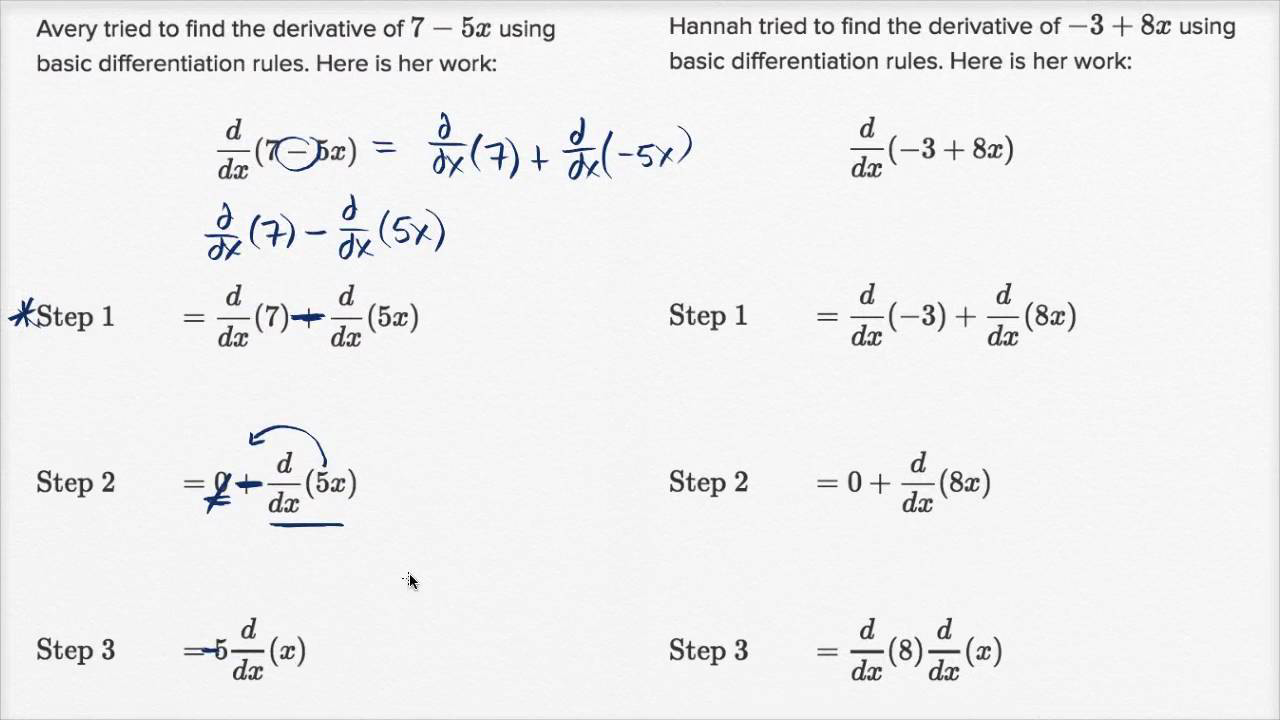
If F (X) = 3 F (X) − 2 G (X) , What Is The Value Of F ′ (8) ?
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Analyze derivatives of functions at specific points as the slope of the lines tangent to the functions' graphs at those points. Let's dive deeper into the fascinating world of derivatives, specifically focusing on the derivative of aˣ for any positive base a. Here we go over many different ways to extend the idea of a derivative to higher dimensions, including partial derivatives , directional.
Learn How To Take Derivatives In Calculus With Khan Academy's Comprehensive Guide.
The big idea of differential calculus is the concept of the derivative, which essentially gives us the direction, or rate of change, of a function at any. If you're behind a web filter, please. Consider the functions f and g with the graphs shown below.