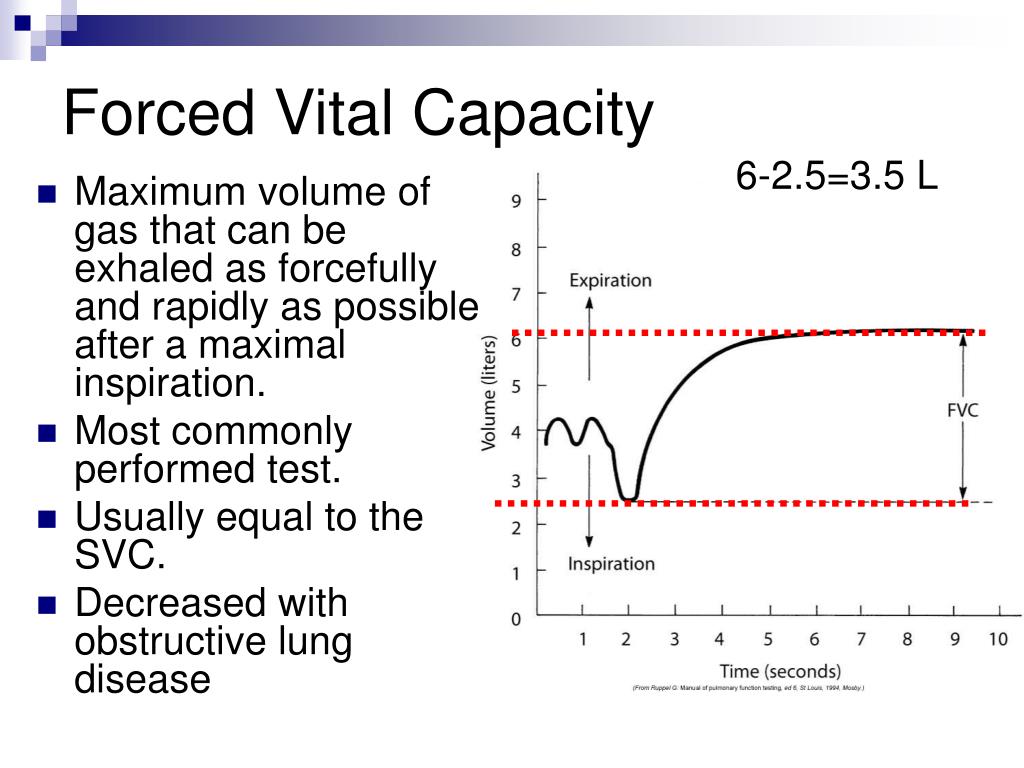
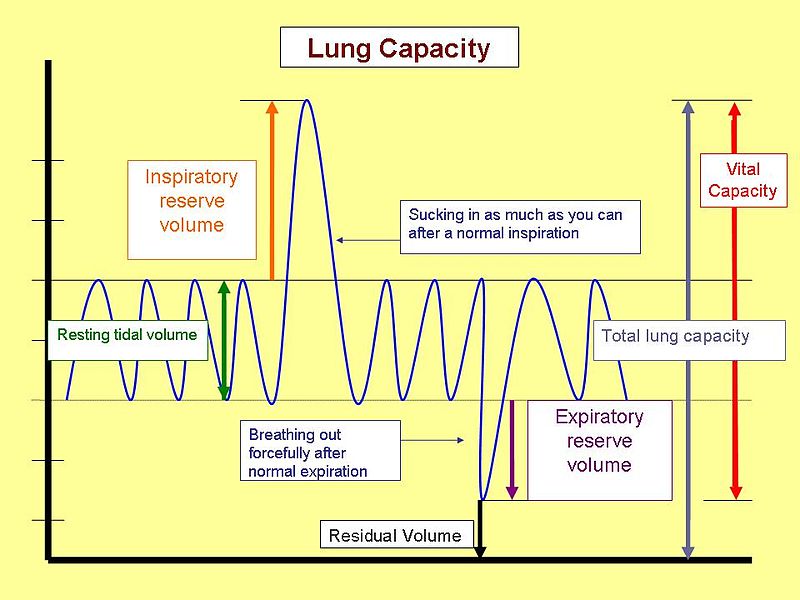
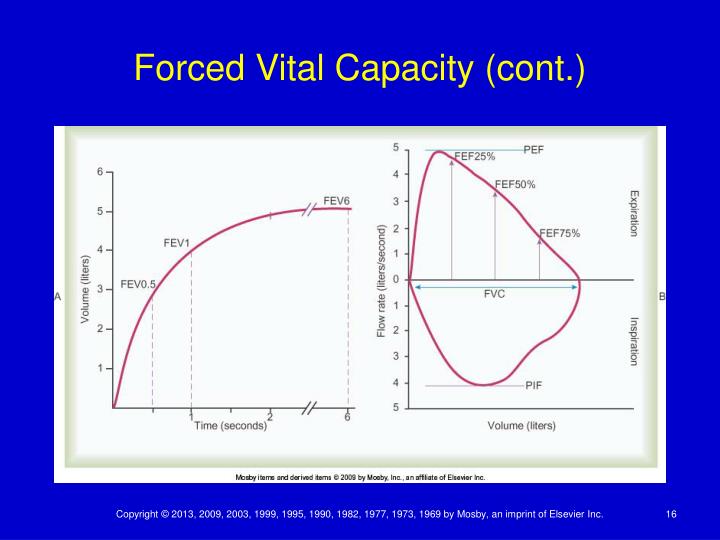
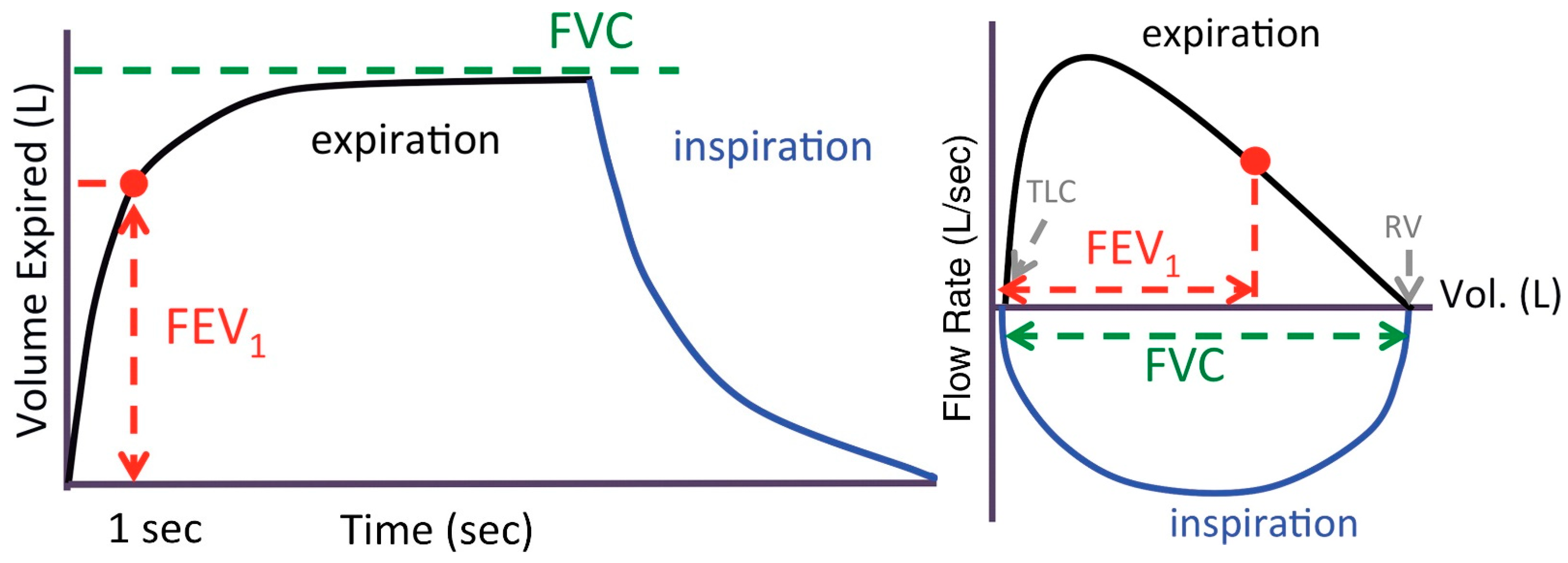
Forced Vital Capacity
Forced Vital Capacity - Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). Vital capacity (vc) is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation. To take a spirometry test, you sit and breathe into a small machine called a spirometer. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled from your lungs after taking the deepest breath possible. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking. It's measured by spirometry, which is. This medical device records the amount of air you breathe in and out as well as. The fvc is similar to vc, but it is measured as the patient. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and.
Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). To take a spirometry test, you sit and breathe into a small machine called a spirometer. The fvc is similar to vc, but it is measured as the patient. It's measured by spirometry, which is. Vital capacity (vc) is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled from your lungs after taking the deepest breath possible. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking. This medical device records the amount of air you breathe in and out as well as.
Vital capacity (vc) is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation. It's measured by spirometry, which is. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled from your lungs after taking the deepest breath possible. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and. To take a spirometry test, you sit and breathe into a small machine called a spirometer. This medical device records the amount of air you breathe in and out as well as. The fvc is similar to vc, but it is measured as the patient. Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking.
Estimated Vital Capacity Formula
Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled from your lungs after taking the.
Vital capacity and the difference Between Forced Vital Capacity and
This medical device records the amount of air you breathe in and out as well as. To take a spirometry test, you sit and breathe into a small machine called a spirometer. Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in.
Difference between Forced Vital Capacity and Vital Capacity
This medical device records the amount of air you breathe in and out as well as. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and. Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). Vital capacity (vc) is the maximum amount of air a person can.
PPT Chapter 19 Pulmonary Function Testing PowerPoint Presentation
This medical device records the amount of air you breathe in and out as well as. The fvc is similar to vc, but it is measured as the patient. Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating.
Understand the importance of forced vital capacity Airofit
Forced vital capacity (fvc) is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled from your lungs after taking the deepest breath possible. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and. To take a spirometry test, you sit and breathe into a small machine called a spirometer. Vital capacity (vc) is the maximum amount of.
Vital Capacity
It's measured by spirometry, which is. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking. Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). It is equal to the sum of inspiratory.
Forced vital capacity evolution. Forced vital capacity (FVC) is
Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). It's measured by spirometry, which is. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking. To take a spirometry test, you sit and.
PPT Pulmonary Function Testing Clinical Physiology PowerPoint
It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and. It's measured by spirometry, which is. This medical device records the amount of air you breathe in and out as well as. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs.
Computers Free FullText Assessment of MultiLayer Perceptron
Forced vital capacity (fvc) is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled from your lungs after taking the deepest breath possible. It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and. The fvc is similar to vc, but it is measured as the patient. It's measured by spirometry, which is. Vital capacity (vc) is the.
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC) An Overview (2024)
Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking. Forced vital capacity (fvc) is the amount of air that can be forcibly exhaled from your lungs after taking the deepest breath possible. Vital capacity (vc) is the maximum amount of air a.
Forced Vital Capacity (Fvc) Is The Amount Of Air That Can Be Forcibly Exhaled From Your Lungs After Taking The Deepest Breath Possible.
Forced vital capacity (fvc) is a crucial measure in respiratory physiology, indicating the maximum volume of air a person can forcibly exhale from their lungs after taking. The fvc is similar to vc, but it is measured as the patient. Vital capacity (vc) is the maximum amount of air a person can expel from the lungs after a maximum inhalation. To take a spirometry test, you sit and breathe into a small machine called a spirometer.
This Medical Device Records The Amount Of Air You Breathe In And Out As Well As.
It's measured by spirometry, which is. Vital capacity may be measured as inspiratory vital capacity (ivc), slow vital capacity (svc), or forced vital capacity (fvc). It is equal to the sum of inspiratory reserve volume, tidal volume, and.