Dual Slack Variable
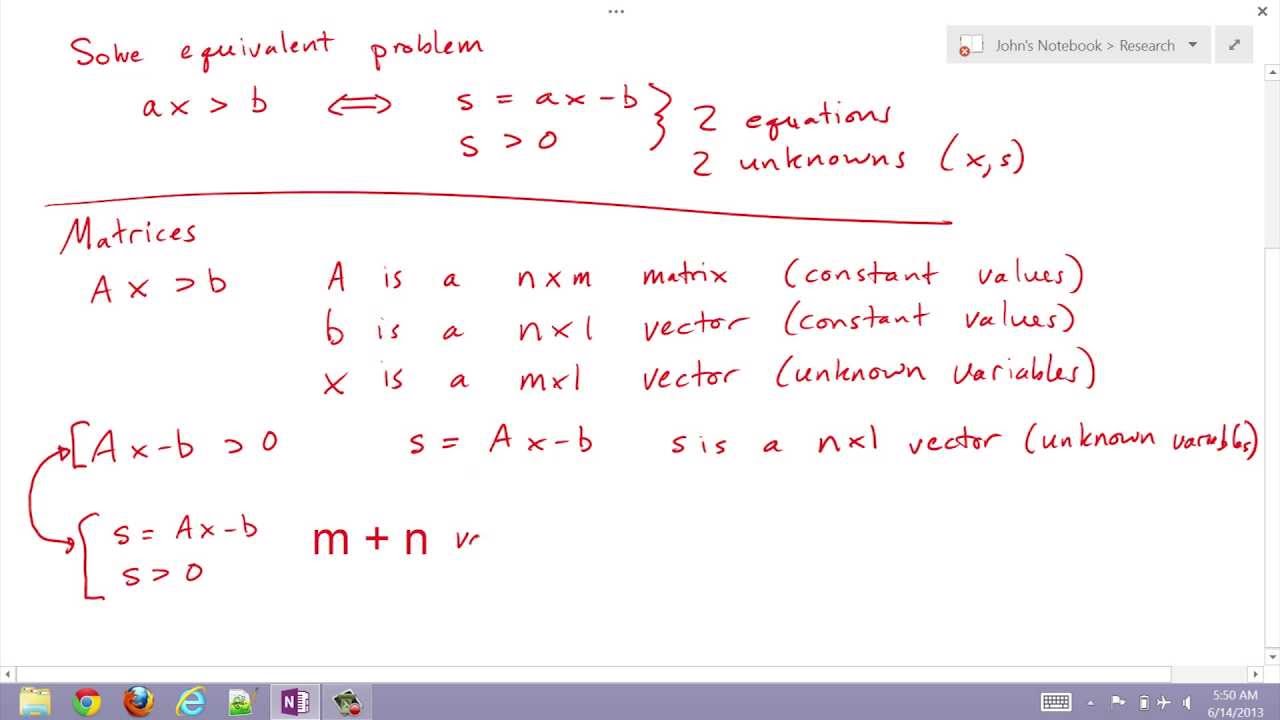
Dual Slack Variable - The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. Since the marginal revenue of a slack activity is zero, its. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for each s. The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. X4 and x5 are somewhat different, since slack variables represent unused capacity.
Since the marginal revenue of a slack activity is zero, its. We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. X4 and x5 are somewhat different, since slack variables represent unused capacity. The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for each s. The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met.
In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for each s. The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. Since the marginal revenue of a slack activity is zero, its. We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. X4 and x5 are somewhat different, since slack variables represent unused capacity.
The minimum cost flow problem ppt download
The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. X4 and x5 are somewhat different, since slack variables represent unused capacity. Since the marginal revenue of a slack activity is zero, its. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of.
Slack or Surplus (Dual Analysis) Variable Row Slack or Surplus Dual
The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. X4 and x5 are somewhat different, since slack variables represent unused capacity. In the dual problem.
The minimum cost flow problem ppt download
We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. Since the marginal revenue of a slack activity is zero, its. The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. In the dual.
Slack Logo (PNG e SVG) Download Vetorial Transparente
The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. X4 and x5 are somewhat different, since slack variables represent unused capacity. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for.
Let A ? Rmxn and let (A2)i denote the ith component
The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for each s. We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but.
Slack Variables YouTube
The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. Since the marginal revenue of a slack activity is zero, its. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for each.
Dual Slack by eking on DeviantArt
We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables.
Difference between Slack and Surplus variable in Simplex method (LPP
In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for each s. We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. X4 and x5 are somewhat different, since slack.
The minimum cost flow problem ppt download
We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables.
Initial Simplex Tableau setup Artificial Variables, Slack, Surplus
We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the. The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables.
Since The Marginal Revenue Of A Slack Activity Is Zero, Its.
The lp maximization problem and its dual above can be converted to an equivalent lp with equality constraints by adding slack variables. The following result refers to the slack variables of the primal and dual, which indicate “by how much” a constraint is met. In the dual problem we define a second variable for each of the variables of the primal including the slack variables, here, a y variable for each s. We don't typically add slack variables to the dual, but if we did, it would have an identical (but slightly sillier) effect on the.