Cognitive Learning Definition
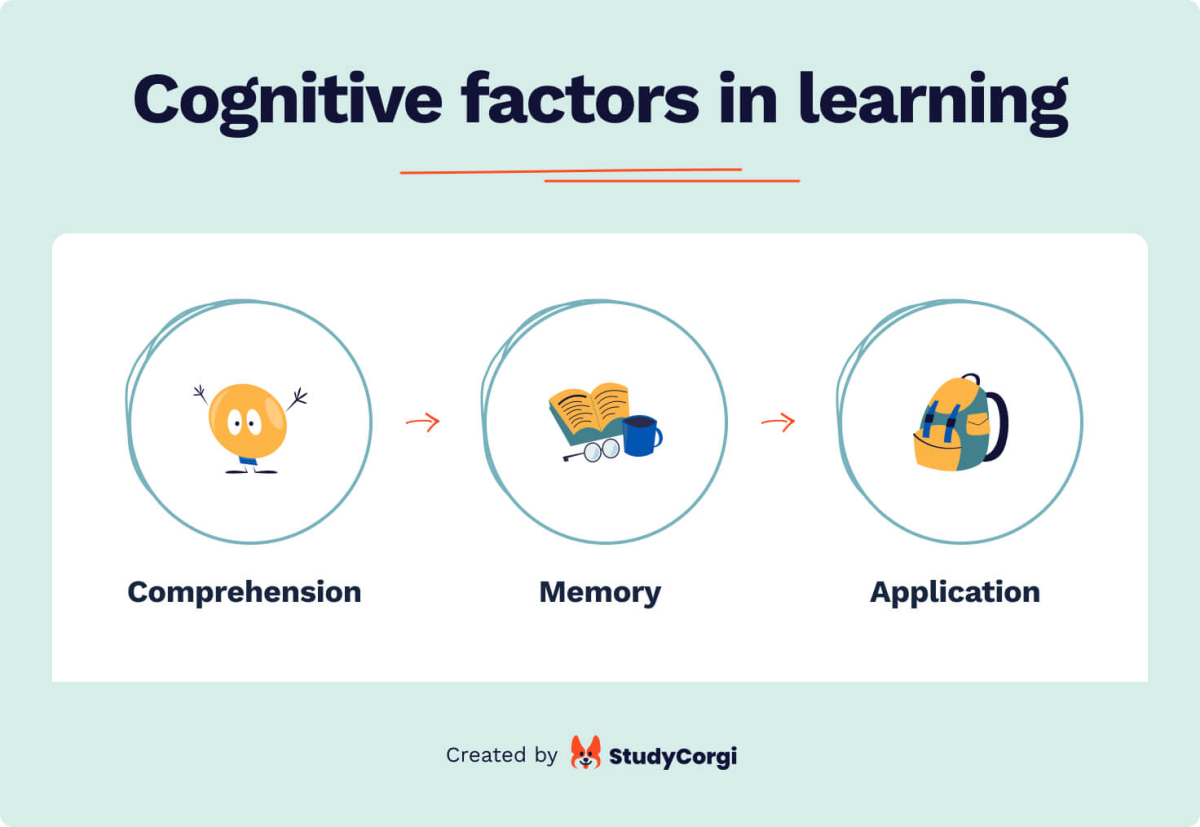
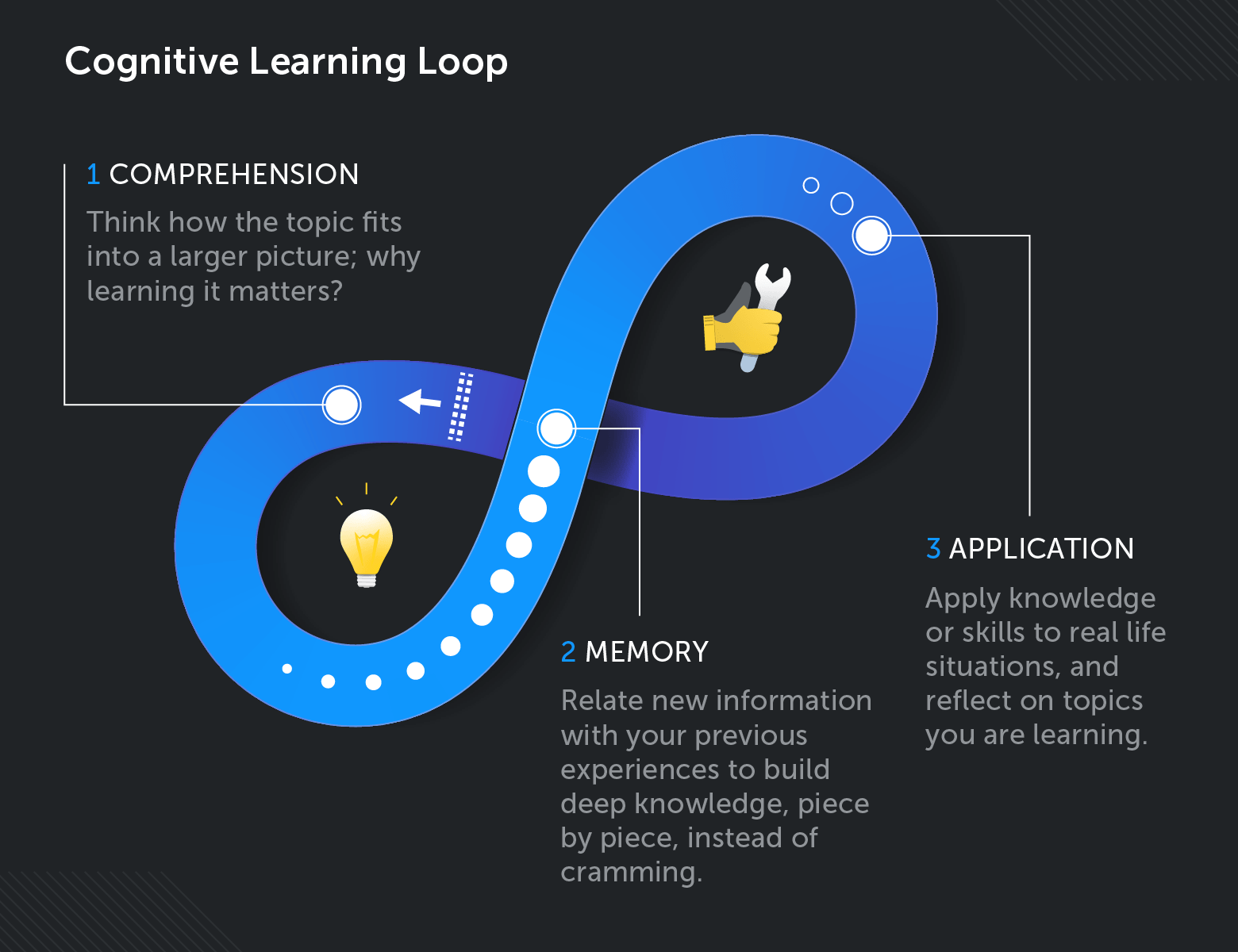
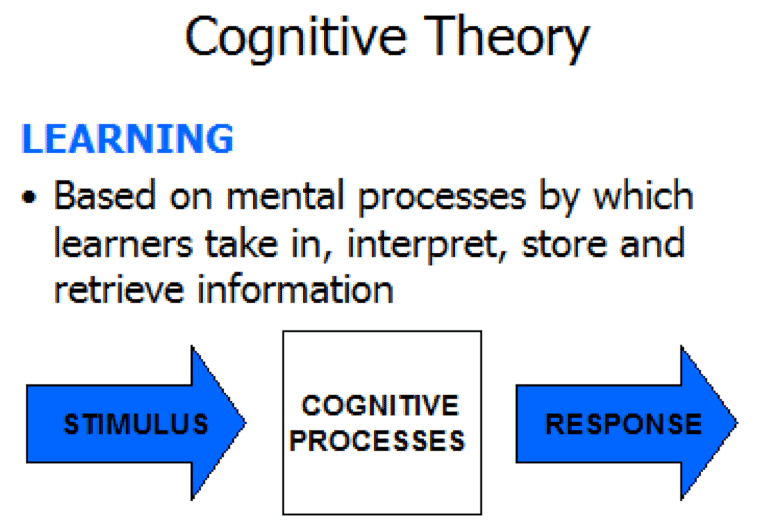
Cognitive Learning Definition - Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge.
Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge.
Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge. It encompasses the ways in which.
PPT Cognitivism PowerPoint Presentation ID302356
Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge. It encompasses the ways in which.
Cognitive Learning Theory Definition & Examples University of Phoenix
Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge.
Piaget's 4 Stages of Cognitive Development Explained
It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge.
Cognitive Skills What They Are and Why They Are Important Edublox
Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. It encompasses the ways in which.
Cognitive Learning 3 Factors, 5 Benefits, & 6 Cognitive Learning
It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge.
Cognitive Learning Theory Benefits, Strategies and Examples
It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing.
29 Cognitive Learning Examples (2024)
It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing.
AP Psychology Study Resource Cognitive Learning AP Psychology Community
It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge.
Cognitive learning theory benefits and examples
Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge. It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing.
Premium Vector Cognitive learning theory educational psychology
It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge. Cognitive learning means gaining knowledge through thinking and understanding, rather than just memorizing.
Cognitive Learning Means Gaining Knowledge Through Thinking And Understanding, Rather Than Just Memorizing.
It encompasses the ways in which. Cognitive learning refers to the mental processes involved in acquiring, retaining, and applying knowledge.
/2795457-article-piagets-stages-of-cognitive-development-5a95c43aa9d4f900370bf112.png)